Virtual Reality vs. Augmented Reality: A Comprehensive Comparison

Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are two cutting-edge technologies that have revolutionized the way we interact with the digital world. In this comprehensive article, I’ll delve deep into the realms of VR and AR, exploring their definitions, evolution, applications, hardware, user experiences, challenges, and much more. By the end of this journey, you’ll have a clear understanding of the differences between these two immersive technologies and be better equipped to decide which one suits your needs or interests.
What Is Virtual Reality?
Let’s start by exploring what Virtual Reality, often abbreviated as VR, really is. VR is a technology that creates a simulated environment, completely different from the real world. It typically involves the use of a head-mounted display (HMD) and can include other sensory feedback devices like haptic gloves or motion trackers. When I engage with VR, I’m transported to a computer-generated 3D world where I can interact with the environment in real-time. This technology aims to provide a completely immersive experience, shutting out the physical world entirely.
What Is Augmented Reality?
Now, let’s turn our attention to Augmented Reality, or AR for short. AR, in contrast to VR, blends digital elements with the real world. Unlike VR, AR does not replace my surroundings but enhances them by overlaying computer-generated images, sounds, or data onto the real environment. When I experience AR, I’m often using mobile apps or specialized AR glasses, which allow me to see both the digital and physical worlds simultaneously. This technology is designed to provide an augmented perception of reality rather than a complete escape from it.
The Evolution of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Both VR and AR have come a long way since their inception. To appreciate their current state, it’s essential to understand their evolution.
VR Evolution
Early Beginnings
Virtual Reality can trace its roots back to the mid-20th century when scientists and engineers began experimenting with the concept of immersive experiences. These early attempts were quite crude by today’s standards, but they laid the foundation for future advancements.
Rise of HMDs
The development of Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) in the 1990s marked a significant milestone for VR. These devices allowed users to wear a headset that covered their eyes and ears, creating a more immersive experience.
Modern VR
Today, VR has evolved into a sophisticated technology used in various industries, from gaming to healthcare. High-quality graphics, precise tracking, and realistic simulations have made modern VR a compelling and accessible technology.
AR Evolution
Origins in Research
Augmented Reality had its beginnings in research labs, with early experiments focusing on overlaying digital information onto real-world objects. These experiments paved the way for practical applications.
Rise of Mobile AR
The proliferation of smartphones brought AR to the masses. Mobile AR apps, such as Pokemon Go, introduced millions of people to the concept of blending digital and physical realities.
AR Glasses
Recent years have seen the development of AR glasses like Google Glass and Microsoft HoloLens. These wearable devices promise to take AR to new heights by seamlessly integrating digital elements into everyday life.
Hardware and Devices
When it comes to experiencing VR and AR, the choice of hardware and devices plays a crucial role. Let’s explore the options available for both technologies.
VR Hardware
Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs)
HMDs are the primary hardware used for VR experiences. They come in various forms, from tethered devices like the Oculus Rift to standalone ones like the Oculus Quest. Tethered HMDs offer high-quality experiences but require a powerful PC, while standalone ones are more accessible and portable.
Motion Controllers
Motion controllers are essential for interacting with VR environments. They allow users to manipulate objects and navigate the virtual world. These controllers come in various designs, offering different levels of immersion.
Haptic Feedback Devices
To enhance immersion, some VR setups include haptic feedback devices. These devices provide tactile feedback, such as vibrations, to simulate touch and texture in the virtual world.
AR Hardware
Smartphones and Tablets
Most people experience AR through their smartphones or tablets. These devices have cameras and sensors that enable AR apps to overlay digital content onto the real world.
AR Glasses
AR glasses, like the Microsoft HoloLens or the rumored Apple AR glasses, are dedicated devices designed explicitly for augmented reality. They offer a hands-free AR experience and are poised to change how I interact with digital information.
AR Headsets
Similar to VR HMDs, AR headsets provide a more immersive AR experience. They typically include cameras and sensors to scan the environment and overlay digital elements accordingly.
In the hardware department, VR has a broader range of options, from high-end HMDs to budget-friendly choices, whereas AR relies heavily on smartphones and is just beginning to explore dedicated devices.
Applications in Gaming
Gaming has been a driving force behind the development of both VR and AR technologies. Let’s take a closer look at how these technologies have influenced the gaming industry.
VR in Gaming
Immersive Worlds
VR has taken gaming to a whole new level by immersing players in virtual worlds. Games like “Half-Life: Alyx” and “Beat Saber” have showcased the potential of VR for gaming.
Enhanced Interactivity
With motion controllers and haptic feedback, VR offers a level of interactivity that traditional gaming cannot match. Players can physically reach out, grab objects, and engage in lifelike combat.
VR Esports
The competitive gaming scene has embraced VR with the rise of VR esports. Tournaments featuring VR games attract skilled players and enthusiastic audiences.
AR in Gaming
Pokemon Go Phenomenon
“Pokémon Go” was a global sensation that introduced AR gaming to the masses. Players used their smartphones to hunt for virtual Pokémon in the real world, creating a novel and engaging experience.
Location-Based AR Games
AR has the potential to create location-based gaming experiences, where the real world becomes the game board. This opens up exciting possibilities for exploration and discovery.
Mixed Reality Games
Some games blur the line between VR and AR, creating mixed reality experiences. These games allow players to interact with both virtual and real objects simultaneously.
Applications in Education
The educational sector has also embraced VR and AR for their potential to transform learning experiences.
VR in Education
Immersive Learning
VR can transport students to historical events, scientific phenomena, or even fictional worlds. This immersive learning can make subjects come to life.
Simulations and Training
In fields like medicine and aviation, VR simulations provide a safe and realistic environment for training. Medical students can practice surgeries, and pilots can hone their skills in a virtual cockpit.
Language Learning
Language learners can benefit from VR language labs, where they can interact with native speakers in virtual settings, improving their language skills.
AR in Education
Interactive Textbooks
AR can transform traditional textbooks into interactive learning experiences. Students can use AR apps to access additional information, videos, and 3D models directly from their textbooks.
Anatomy and Biology
In anatomy classes, AR apps can overlay 3D models of the human body onto textbooks, giving students a better understanding of complex structures.
Historical Augmentation
AR can bring history to life by overlaying historical images, videos, and information onto real-world landmarks or artifacts.
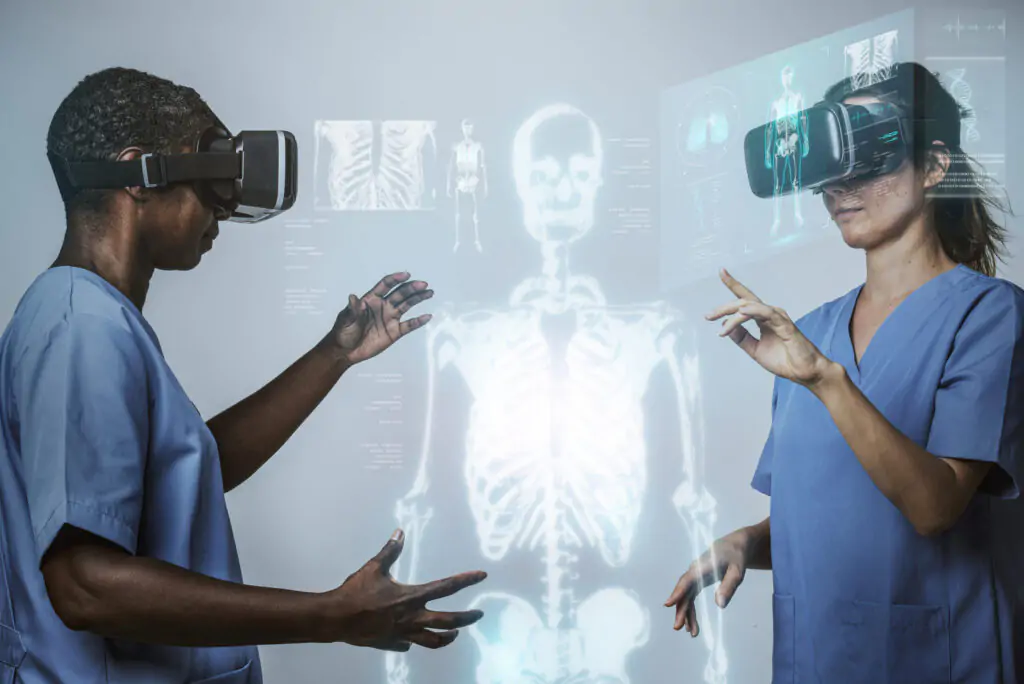
Applications in Healthcare
VR and AR have made significant contributions to the field of healthcare, from medical training to patient care.
VR in Healthcare
Surgical Training
Surgeons can practice complex procedures in a risk-free VR environment, improving their skills and reducing the risk to patients.
Pain Management
VR has been used as a distraction technique for patients undergoing painful procedures. Immersive experiences can help reduce pain perception.
Exposure Therapy
VR is utilized in exposure therapy to treat phobias and PTSD. Patients can confront their fears in a controlled virtual environment.
AR in Healthcare
Vein Visualization
AR glasses can assist medical professionals in locating veins for blood draws and IV placements, reducing discomfort for patients.
Real-time Information
Doctors can access patient information and relevant data in real-time through AR glasses, improving decision-making during surgeries.
Rehabilitation
AR can be used in rehabilitation exercises, providing visual feedback and motivation for patients recovering from injuries.
Industrial and Business Uses
Both VR and AR have found applications in various industries, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
VR in Industry
Virtual Prototyping
Manufacturers can create virtual prototypes of products, saving time and resources in the design process.
Employee Training
VR is used for employee training in industries like manufacturing and construction, where hands-on experience is critical.
Remote Collaboration
VR allows teams to collaborate in a virtual space, making it easier for remote workers to work together effectively.
AR in Industry
Maintenance and Repair
AR glasses can provide technicians with step-by-step instructions and visual aids for equipment maintenance and repair.
Inventory Management
AR can streamline inventory management by providing real-time data and visual overlays for locating items in warehouses.
Field Support
Field workers can benefit from AR glasses that provide them with relevant information and guidance while on-site.
Entertainment and Media
The entertainment and media sectors have embraced VR and AR to create immersive and engaging experiences for audiences.
VR in Entertainment
Virtual Concerts
VR allows music lovers to attend virtual concerts and festivals, enjoying a front-row seat from the comfort of their homes.
Cinematic VR
Filmmakers have explored VR as a new storytelling medium, creating immersive cinematic experiences that place viewers inside the story.
Theme Park Attractions
Theme parks incorporate VR into rides and attractions, adding an extra layer of excitement to the visitor experience.
AR in Entertainment
Interactive Advertising
AR is used in marketing and advertising to create interactive campaigns. Consumers can use their smartphones to unlock AR content from advertisements.
Location-Based Experiences
Entertainment venues like museums and theaters use AR apps to enhance visitors’ experiences by providing additional information and interactive elements.
Augmented Reality Games
AR gaming experiences, like “Harry Potter: Wizards Unite,” merge the real world with the fictional, encouraging players to explore their surroundings.
Social Interaction and Communication
VR and AR are changing the way we connect with others in the digital realm.
VR for Social Interaction
Virtual Hangouts
Social VR platforms like VRChat and Rec Room allow users to meet, interact, and socialize in virtual environments.
Long-Distance Relationships
Couples in long-distance relationships can use VR to feel more connected by sharing virtual spaces and activities.
Virtual Conferences
VR is becoming a popular choice for virtual conferences and events, offering attendees a more immersive and engaging experience.
AR for Social Interaction
Augmented Social Media
AR filters and effects on social media platforms like Instagram and Snapchat enable users to express themselves creatively and connect with friends.
Location-Based Social Apps
AR apps like Pokemon Go foster social interactions by encouraging players to team up and explore their neighborhoods together.
Enhanced Video Calls
AR features in video conferencing apps can make virtual meetings more engaging and interactive.
User Experience and Immersion
Both VR and AR are designed to offer unique and immersive user experiences, but they achieve this in different ways.
VR User Experience
Total Immersion
VR aims to completely immerse users in a digital environment, shutting out the real world and replacing it with a simulated one.
Presence
Presence refers to the feeling of “being there” in the virtual world. Achieving presence is a key goal in VR development.
Motion Sickness
Some users may experience motion sickness in VR due to a disconnect between visual and vestibular cues. Developers are continually working to minimize this issue.
AR User Experience
Blended Reality
AR enhances the real world with digital elements, allowing users to maintain awareness of their physical surroundings.
Contextual Information
AR provides users with contextually relevant information based on their environment, enhancing their understanding and decision-making.
Accessibility
AR is more accessible as it can be experienced through smartphones, making it easier for a broader audience to engage with the technology.
Cost Considerations
The cost of adopting VR and AR technologies can vary significantly, affecting their accessibility to individuals and businesses.
VR Costs
Hardware Expenses
Investing in high-quality VR hardware, such as top-tier HMDs and powerful PCs, can be costly.
Software and Content
VR software and content, including games and applications, also come at a price, although there is a growing library of free experiences.
Ongoing Maintenance
Maintaining VR hardware and keeping up with software updates can incur additional costs.
AR Costs
Smartphone Integration
AR is more accessible as it often relies on smartphones, which many people already own.
AR Glasses Expenses
While AR glasses offer a more immersive experience, they can be expensive, limiting their adoption.
App Costs
AR app development and subscriptions to AR services can add to the overall cost.
Development and Programming
Creating content for VR and AR requires specialized skills and tools.
VR Development
Game Engines
VR developers often use game engines like Unity or Unreal Engine to create immersive experiences.
3D Modeling
Designing 3D models and environments is a crucial aspect of VR content creation.
Interaction Design
Developers must carefully consider how users will interact with VR environments, which often involves designing intuitive user interfaces.
AR Development
App Development
AR experiences are typically built as mobile apps, requiring expertise in app development.
Markerless Tracking
AR developers work on markerless tracking systems that can recognize and augment objects or locations without relying on markers or QR codes.
Spatial Mapping
Creating accurate spatial maps of the environment is essential for AR apps to overlay digital content seamlessly.
Future Trends and Innovations
The world of VR and AR is constantly evolving, with exciting trends and innovations on the horizon.
VR Trends
Wireless VR
Wireless VR solutions are becoming more prevalent, eliminating the need for tethered headsets and providing greater freedom of movement.
Improved Haptic Feedback
Advancements in haptic feedback technology will enhance the sense of touch in VR experiences, making them even more immersive.
VR in Education
VR is expected to play an increasingly significant role in education, offering students immersive and interactive learning opportunities.
AR Innovations
AR Glasses Evolution
AR glasses are expected to become more lightweight, affordable, and stylish, leading to wider adoption.
AR in Navigation
AR navigation systems could revolutionize how people navigate cities and public spaces, providing real-time directions and information.
AR in Retail
AR is poised to transform the retail experience, allowing customers to try products virtually before making a purchase.
Challenges and Limitations
While VR and AR offer incredible potential, they also face challenges and limitations.
VR Challenges
Motion Sickness
Motion sickness remains a significant challenge, especially in VR experiences with intense movement.
High Hardware Costs
The cost of high-quality VR hardware can be a barrier to entry for many potential users.
Limited Real-World Interaction
VR isolates users from the physical world, which can be a limitation in certain scenarios.
AR Challenges
Privacy Concerns
AR raises privacy concerns as it involves overlaying digital information onto the real world, potentially impacting personal privacy.
App Dependence
AR relies heavily on the availability of compatible apps, limiting its functionality without the right software.
Safety Concerns
AR glasses and apps can be distracting, potentially leading to safety concerns, especially while driving or walking in busy areas.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
As VR and AR become more integrated into daily life, ethical and privacy considerations come to the forefront.
VR Ethics
Psychological Impact
Extended use of VR can have psychological effects, such as detachment from reality or addiction-like behaviors.
Content Regulation
VR content can range from harmless entertainment to graphic violence, prompting discussions about content regulation.
Identity and Anonymity
In VR social spaces, issues of identity and anonymity can arise, leading to ethical dilemmas.
AR Ethics
Privacy Invasion
AR apps that collect and use personal data raise concerns about privacy invasion.
Digital Manipulation
AR can be used for digital manipulation, altering the appearance of people and objects in real-time.
Augmented Reality Crime
AR opens up new possibilities for cybercrimes, such as virtual graffiti or vandalism.
Adoption and Market Share
The adoption of VR and AR technologies varies by industry and region.
VR Adoption
Gaming Dominance
VR has seen widespread adoption in the gaming industry, with a growing library of VR games and experiences.
Niche Markets
While VR has made strides in education, healthcare, and training, it remains somewhat niche in these sectors.
High-End Consumers
VR is popular among high-end consumers who invest in premium VR hardware for gaming and entertainment.
AR Adoption
Consumer-Focused
AR is more consumer-focused, with applications in entertainment, social media, and everyday smartphone use.
Retail and Marketing
AR has found applications in retail and marketing, enhancing the shopping experience and engagement with brands.
Enterprise Solutions
AR is gaining traction in enterprise settings, particularly for training and field support.
Industry Players
Several companies and organizations are leading the charge in the development and promotion of VR and AR technologies.
VR Industry Players
Oculus (by Facebook)
Oculus has been a major player in the VR industry, producing popular VR headsets like the Oculus Rift and Oculus Quest.
HTC Vive
HTC Vive is known for its high-end VR hardware, catering to enthusiasts and professionals.
Sony PlayStation VR
Sony’s PlayStation VR has brought virtual reality gaming to millions of PlayStation users.
AR Industry Players
Apple
Apple is rumored to be working on AR glasses, and its ARKit framework has enabled AR experiences on iOS devices.
Google’s ARCore platform powers AR experiences on a wide range of Android devices.
Microsoft
Microsoft’s HoloLens is a pioneering AR headset used in various industries, including healthcare and manufacturing.
Which Is Better for Gaming?
The debate over whether VR or AR is better for gaming is ongoing, and the answer depends on personal preferences and the type of gaming experience one seeks.
VR for Gaming
Immersive Adventures
I believe VR offers unparalleled immersion, making players feel like they are inside the game world.
Intense Interactivity
The motion controllers and haptic feedback in VR provide a level of interactivity that can’t be matched by traditional gaming.
High-Quality Graphics
VR headsets are designed for high-quality graphics and realistic environments, enhancing gaming experiences.
AR for Gaming
Blending with Reality
AR gaming blends the virtual with the real world, creating unique and location-based experiences.
Accessibility
AR gaming is more accessible as it often relies on smartphones, making it easier for a broader audience to participate.
Social Interaction
AR gaming can encourage social interactions, as seen in games like Pokemon Go, where players collaborate and explore together.
Which Is Better for Education?
Both VR and AR have made significant contributions to education, but their strengths lie in different areas.
VR for Education
Immersive Learning
VR offers immersive experiences that can transport students to historical events, scientific phenomena, or even fictional worlds.
Simulation-Based Training
VR is ideal for training in fields like medicine, aviation, and engineering, where hands-on practice is crucial.
Language Learning
Language learners can benefit from VR language labs, where they can practice in realistic scenarios.
AR for Education
Interactive Textbooks
AR can transform traditional textbooks into interactive learning experiences, providing additional information and 3D models.
Real-World Context
AR enhances real-world learning by overlaying digital information onto objects or locations, providing context and insights.
Accessibility
AR is more accessible as it often relies on smartphones, making it easier for schools with limited budgets to adopt the technology.
Which Is Better for Healthcare?
Both VR and AR have made significant strides in healthcare, but their applications differ.
VR in Healthcare
Surgical Training
VR is invaluable for surgical training, allowing surgeons to practice complex procedures in a risk-free environment.
Pain Management
VR can be used as a distraction technique for patients undergoing painful procedures, reducing their perception of pain.
Exposure Therapy
VR is effective in exposure therapy for treating phobias and PTSD by creating controlled virtual environments.
AR in Healthcare
Vein Visualization
AR glasses can assist medical professionals in locating veins for blood draws and IV placements, improving patient comfort.
Real-time Information
AR glasses provide doctors with real-time patient information during surgeries, enhancing decision-making.
Rehabilitation
AR can be used in rehabilitation exercises, offering visual feedback and motivation to patients in recovery.
Which Is Better for Business?
The choice between VR and AR in the business world depends on the specific needs and goals of the organization.
VR for Business
Virtual Prototyping
Manufacturers can use VR for virtual prototyping, saving time and resources in product development.
Employee Training
VR is valuable for employee training in industries like manufacturing, where hands-on experience is essential.
Remote Collaboration
VR enables teams to collaborate in virtual spaces, facilitating remote work and reducing travel costs.
AR for Business
Maintenance and Repair
AR glasses can provide technicians with step-by-step instructions and visual aids for equipment maintenance and repair.
Inventory Management
AR can streamline inventory management by providing real-time data and visual overlays for locating items in warehouses.
Field Support
Field workers can benefit from AR glasses that offer relevant information and guidance while on-site, improving productivity.
Making the Choice: VR or AR?
Ultimately, the choice between VR and AR depends on individual preferences and the intended use case. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Choose VR If:
- You seek complete immersion in a virtual world.
- Intense interactivity and lifelike experiences are important to you.
- High-quality graphics and realistic simulations are your priority.
- You am interested in gaming, cinematic experiences, or simulations.
Choose AR If:
- You want to enhance my real-world surroundings with digital elements.
- Accessibility and smartphone integration are essential.
- You am interested in location-based experiences, social interactions, or everyday applications.
- Practical uses like navigation, retail, or field support that align with your needs.
Final thoughts
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are two remarkable technologies that have transformed industries, entertainment, education, and more. While they share some similarities in terms of immersive experiences, they differ in their approach and applications.
VR immerses users in entirely virtual worlds, making it ideal for gaming, simulations, and immersive training. AR enhances the real world by overlaying digital information, making it more suitable for everyday applications, location-based experiences, and enhancing productivity in various industries.
As both technologies continue to evolve, the choice between VR and AR becomes more about personal preferences, specific use cases, and accessibility. The future holds exciting possibilities for VR and AR, promising to redefine how we interact with the digital and physical worlds.
In summary, VR and AR are not competitors but complementary technologies, each with its unique strengths and applications. Their coexistence offers a diverse range of experiences and opportunities for innovation, shaping the way we interact with technology and the world around us.
 English
English